- Blog
- WLTP Standards – Everything You Need to Know
WLTP Standards – Everything You Need to Know
All the questions you had about the WLTP standard and CO2 emissions answered simply and clearly by eCarsTrade automotive experts.

The Worldwide Harmonised Light Vehicle Test Procedure (WLTP) was introduced in 2018 to ensure car manufacturers respect the limits on CO2 emissions.
As necessary as this measure is, the WLTP standard isn’t always easy to understand and interpret for used car dealers who want to avoid noncompliance and extra fees for their customers.
That’s why we have put together a list of frequently asked questions about WLTP standards and testing and asked eCarsTrade experts to give their experts advice and guidance.
Read our most-asked questions and address your buyers’ concerns with confidence.
Does WLTP testing better reflect real driving conditions?
The testing procedure that was used before the WLTP standard, NEDC (which stands for New European Driving Cycle), was actually very similar to it. NEDC measured the same elements of driving.
However, the NEDC used theoretical, average data to calculate CO2 emissions, while the WLTP uses something called a dynamic cycle.
This dynamic cycle better reflects driving conditions because it measures emissions at different stages of driving: low, medium, high, and extra-high speed.
Moreover, the measured stages also include braking, acceleration, and stopping. As you can imagine, all of this more closely resembles how cars behave on the road.
In addition to that, the WLTP test takes longer and spans more kilometers, which means it’s able to collect more data to analyze for more accurate results.
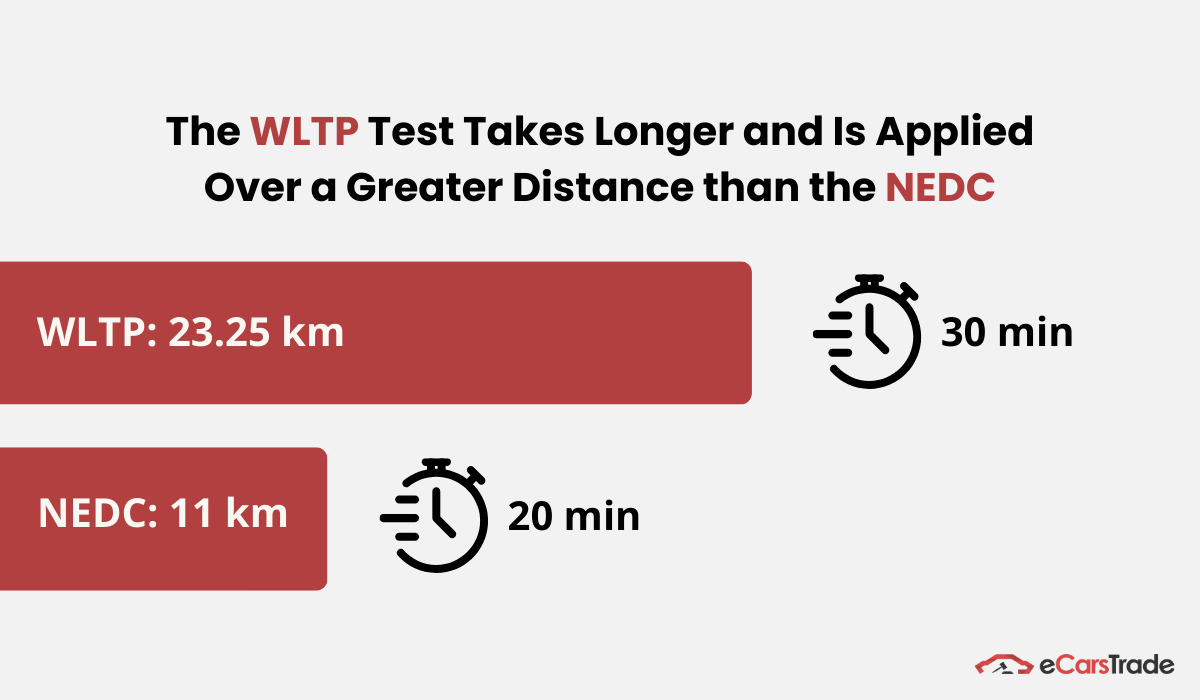
Data: Riverale
The NEDC served its purpose well, but technology advancements enabled us to replicate driving conditions closer, and so the WLTP standard was developed and eventually accepted.
What impact does WLTP have on vehicle tax and registration fees?
To recap, the WLTP standard measures CO2 emissions, among other things. The results of that test determine whether a car is compliant with the current CO2 regulations in a certain EU country.
How does that work? Well, EU countries typically determine “CO2 emission bands” or thresholds for the maximum emission levels acceptable by law. Generally speaking, if the WLTP test result shows emission levels higher than that threshold, the vehicle is taxed higher, and vice versa.
The same goes for registration fees. Registration fees are a one-time tax determined by multiple factors, one of which may be CO2 emissions (measured by the WLTP).
Countries have their own emissions regulations, so you should check what they are and ensure the car you will be selling in that country is CO2 compliant to avoid unexpected fees for your customers.
Are all vehicles subject to WLTP testing, or are there exceptions?
Remember that the WLTP only came into power in 2018. That means that cars manufactured before that will have NEDC values in their documentation (specifically, cars manufactured before September, 2017). That value will be taken into consideration when taxes and fees are calculated.
In other words, only cars from 2018 onwards are subject to WLTP testing, and even then, some country-specific conditions may apply. For example, in Belgium, NEDC values were accepted until January 2021. In the Netherlands, the cut-off date was 1 July 2020.
How do WLTP values compare to real-world emissions and fuel consumption?
One of the reasons WLTP was introduced is because the NEDC, relying on theoretical data, didn’t reflect real-world emissions. The WLTP, on the other hand, is more accurate, and experts are confident that this data is much closer to the true emissions of today’s cars.
A fact that shows this is true is the great discrepancy between NEDC and WLTP test results.
Comparing these two test methods, experts have found that the WLTP reports significantly higher CO2 emission readings, reaching as much as an additional 9.6g of CO2/km!
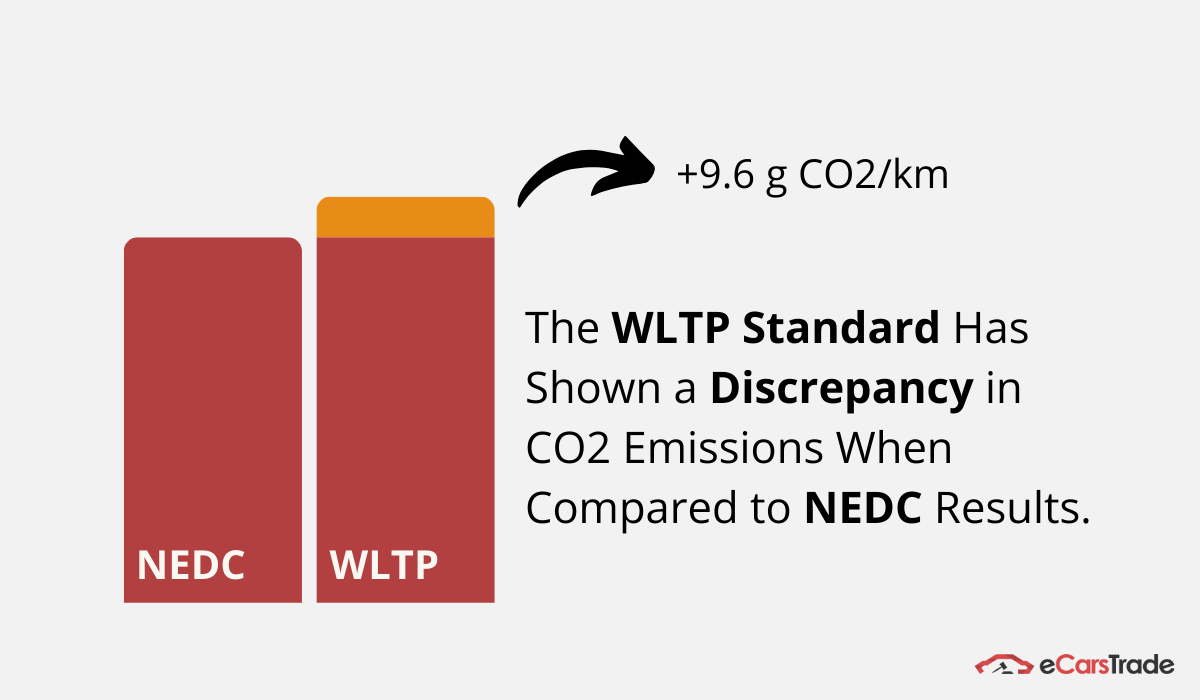
Data: JATO
As the world invests more effort into cutting down traffic CO2 emissions, accurate readings are key to understanding what needs to be done, and the WLTP is a good step in that direction.
What are the key components measured during WLTP testing?
The WLTP is a test that examines different driving cycles, speeds, and car load configurations (extra equipment, for example) to measure - what exactly?
Well, the most obvious answer is CO2 emissions. But the WLTP is actually a more comprehensive test than many realize.
In addition to the CO2 your car is directly responsible for, it also measures the following components:
- Fuel consumption (because the more fuel you burn, the more CO2 you emit)
- Pollutant emissions (harmful particles and gases, nitrous oxides)
By measuring all of these elements, the WLTP can deliver a more complete analysis of the vehicle's effect on the environment.
How should car dealers and consumers interpret WLTP data?
From the perspectives of dealers and consumers, the main objective of the WLTP standard is to provide a clear answer about whether or not a car is CO2 compliant in a certain country or region.
The WLTP value (amount of CO2 emissions in g/km) can be found in the car’s documentation, as well as online resources such as the Belgian car registry.
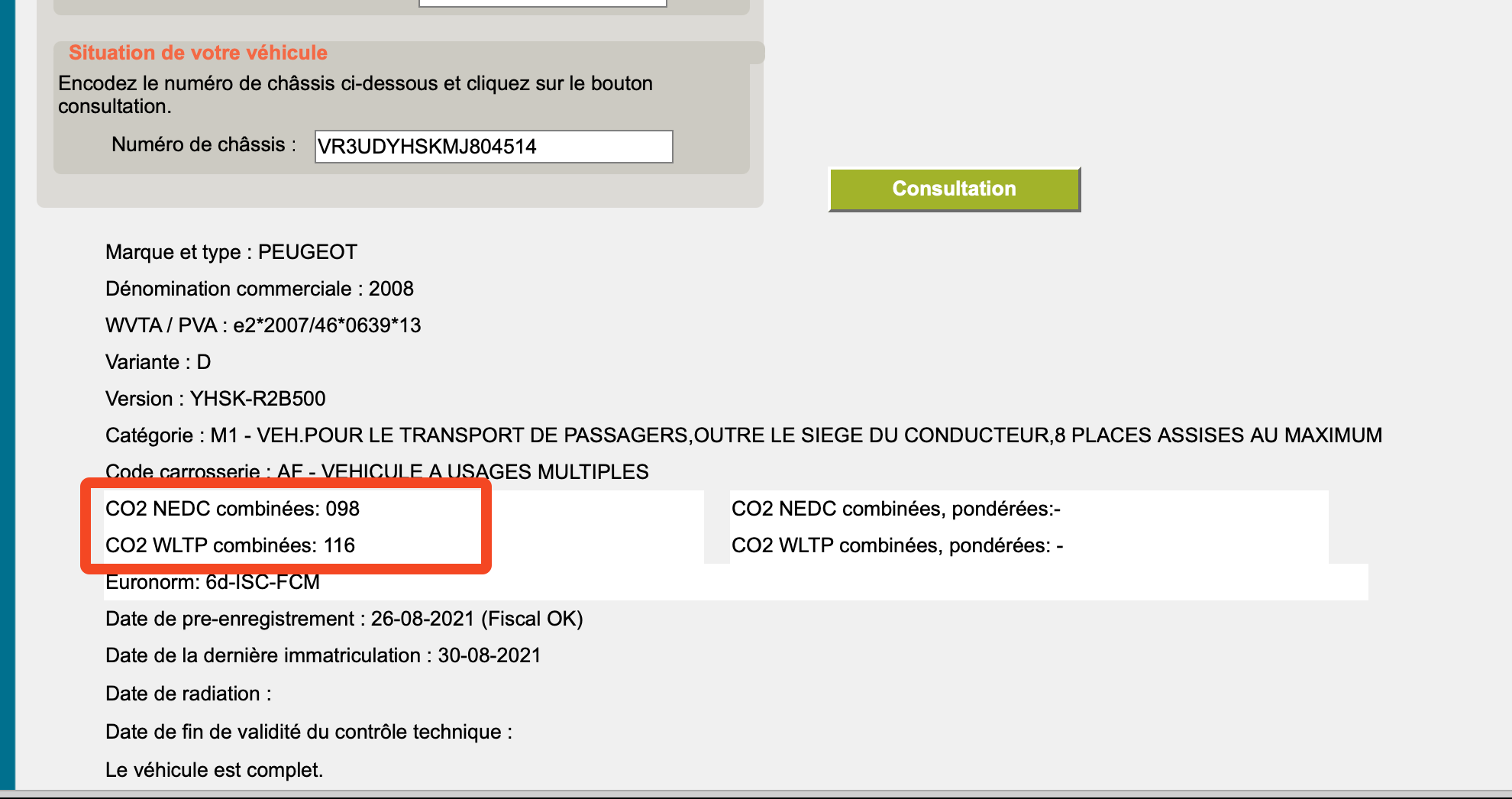 Check your Belgian car's NEDC and WLTP values in the Belgian registry
Check your Belgian car's NEDC and WLTP values in the Belgian registry
The information that will tell you if the car is compliant is the following:
- The car’s first registration date: this will tell you if the WLTP or the NEDC test is applied.
- The CO2 values expressed in the documentation (WLTP or NEDC, whichever is applied).
- The target country’s CO2 regulations (where the car will be sold): so you can compare the values to the regulations.
With this information on hand, you should have no problem interpreting the WLTP values of your car and acting on it to ensure compliance and proper taxation.
What are the implications of WLTP for electric and hybrid vehicles?
Since electric and hybrid vehicles don’t emit as much CO2 as combustion engine vehicles, the WLTP doesn’t apply to them, right?
Actually, it does. And it’s easy to see why.
Electric vehicles may not emit CO2 as a byproduct of burning fuel. However, it’s important to remember that the energy stored in their batteries still had to be created somehow and that that process also results in CO2 emissions.
What does this mean? It means that these vehicles must be included in the WLTP standard.
Here is a video that will show you exactly how this procedure works for these vehicles.
Here’s How Electric Cars Are WLTP / EPA Range Tested!
For hybrid vehicles, the WLTP procedure measures CO2 emissions at full, half-full, and empty (running just on fuel) battery states.
For battery-electric vehicles, the WLTP measures the range of the vehicle on a full battery.
Just like combustion-engine cars, every EV make and model has a set WLTP value it needs to comply with.
How does WLTP affect used car imports and exports in the EU?
As mentioned, different countries in the EU have different CO2 emission regulations. That means that a car you’re importing from another EU country might not be CO2 compliant in your country.
That’s why you should prepare and check local regulations before importing cars to make sure you won’t have to pay extra taxes or registration fees.
Other than that, even though the WLTP was rolled out in 2018, EU countries had the right to delay WLTP implementation.
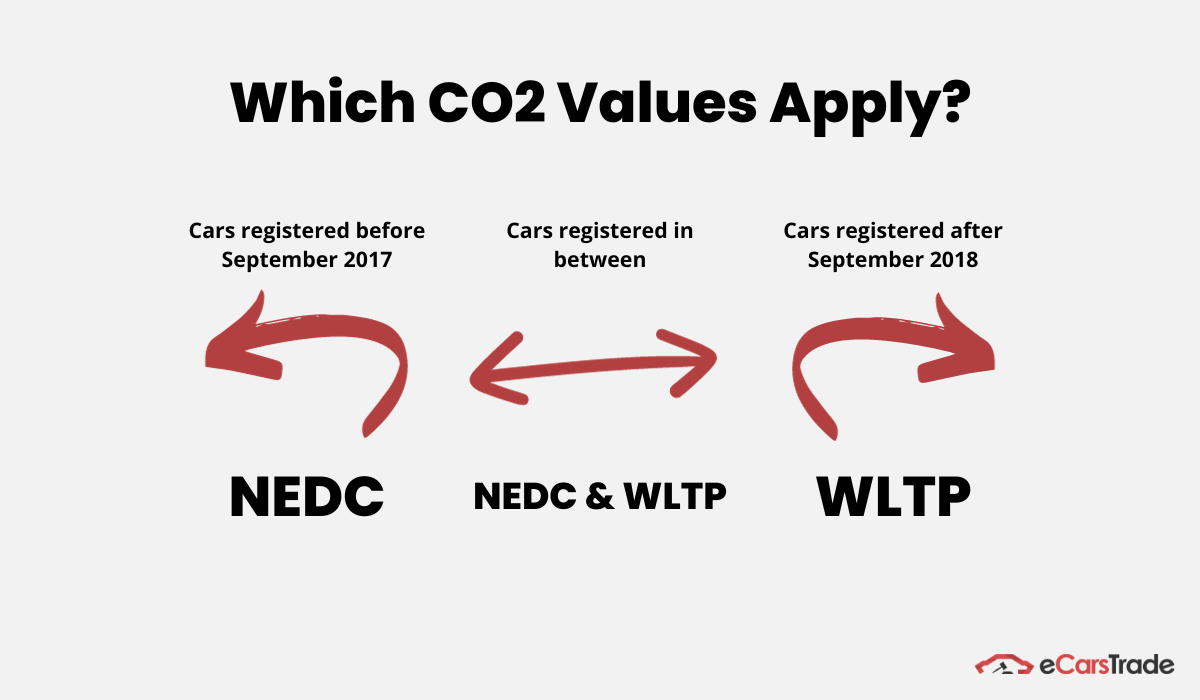
That means that there is a chance that a car’s NEDC value might be taken into consideration at registration, even if it was manufactured after 2018.
You’ll also need to check local regulations to see when exactly WLTP came into power.
How frequently are WLTP testing methods updated or revised?
The WLTP is a relatively new standard, and we anticipate it will remain stable for many years because it has proven reliable so far.
However, as with any scientific method, improvements to the standard are possible, though they aren’t likely to significantly change the test.
The acceptable levels of CO2 emissions in new cars change every couple of years.
Regulations will continue decreasing acceptable levels of CO2 emissions to align with EU efforts to cut down on emissions. Car manufacturers will need to develop new ways to lower this harmful effect of driving.
What future developments are expected in emission testing standards beyond WLTP?
With CO2 emissions adequately tested and standardized, the automotive industry and EU legislation will likely develop new tests that more accurately measure other driving factors, such as particulate matter.
We can also expect measurements for emissions that don’t come from burning fuel, such as emissions from tire wear and braking.
Finally, as EVs become more present on EU roads, we could soon see testing more adapted to these vehicles, such as standards related to EV battery manufacturing, use, and disposal.
More Questions About WLTP? Ask eCarsTrade Experts!
This post covered the questions about WLTP that our buyers often ask when buying EU-sourced used vehicles on eCarsTrade.
From test result interpretation to standard application across vehicles of all makes, models, and engine types, we have been able to find accurate information to ensure our customers are always compliant with regulations.
Our customer service and Account Managers are available throughout the purchasing journey, so browse our offer today and contact us with any questions you have about your car’s CO2 emissions.



